A data governance policy is a documented set of guidelines that ensure an organization’s information assets are managed consistently.
In this article, we’ll explore the concept of data governance policy and its types, check out some examples of good data governance policies, and provide a draft template to get started on yours.
See How Atlan Simplifies Data Governance – Start Product Tour
Data governance policy outlines the rules of engagement with data, overseeing how you access data assets and what operations you carry out on those assets. It ensures compliance with internal rules and applicable legislation and standards.
Effective data governance policies help establish a framework for managing data assets consistently while supporting strategic business objectives.
Additionally, they help you understand what data governance procedures are in place (and why), who is responsible for them, and how they should be managed.
Since data governance as a principle includes directives across people, processes, and technologies, data governance policies should be equally comprehensive.
Gartner identifies six data governance policy types — data quality, privacy, security, lifecycle, ethics, and definitions and models.
Let’s explore the specifics of each policy to flesh out the role they play in data governance:
Establishing and implementing data governance policies includes two stages:
In this article, we’ll look into the data governance policy-setting process. We’ll discuss data governance policy enforcement in subsequent articles.
Data governance policy setting is the responsibility of business leaders who are part of one or more governance boards or teams. So, building a cross-functional team involving the right people is an excellent way to start.
You should identify key stakeholders for each data governance policy type, such as:
This is also the stage to establish accountability — map roles and responsibilities for the various data governance functions.
The goal of data governance policy setting is to establish data governance policies as well as KPIs to monitor their adoption and enforcement in a collaborative, data-driven manner.
Setting data governance policies involves the following steps:
Let’s explore the specifics.
Asking these questions can help you set effective policies:
The next step is to draft a policy document.
Data governance policies must translate into tangible benefits for your business. Without a clear connection to business outcomes, data governance would be an administrative burden with no real payoff.
For example, your policy on data quality should be tied to business outcomes such as reduced costs or improved efficiency (faster product development cycle, for instance). Data privacy policy could translate to customer trust, brand loyalty, and no hefty GDPR fines.
Meanwhile, clear guidelines on data retention, archival, and deletion (i.e., data lifecycle policy) can translate to lower storage costs and improved compliance.
Next, let’s look at drafting a data governance policy document.
Eugenia Moore, Manager of Data Governance and Quality at Peapod Digital Labs, recommends drafting a short, precise data governance policy document with the following sections:
Once you’ve drafted the document, the next step is to set things in motion. That’s where an active data governance tool can help.
Since setting and enforcing data governance policies is a collaborative process with numerous stakeholders across teams, using an active data governance platform makes it seamless and efficient.
For instance, a platform like Atlan offers a bird’s-eye view of all the data governance policy workflows, metrics, and dashboards at a glance under Policy Center.
More importantly, data governance policy setting is incomplete without connecting to the right business outcomes. That’s where Atlan stands out — we connect policies to data.
You can connect new policies to pre-defined policy types (quality, privacy, security, etc.) and identify the data domains, user roles, or groups that will adhere to them.
You can also use Atlan to draft policy documents, set up approval workflows, monitor policy adoption and enforcement metrics, and more.
Let’s walk through a basic policy-setting workflow to understand how Atlan helps set and enforce data governance policies.
Note: When setting a new policy, you must draft the policy and then an approval workflow before enforcing it.
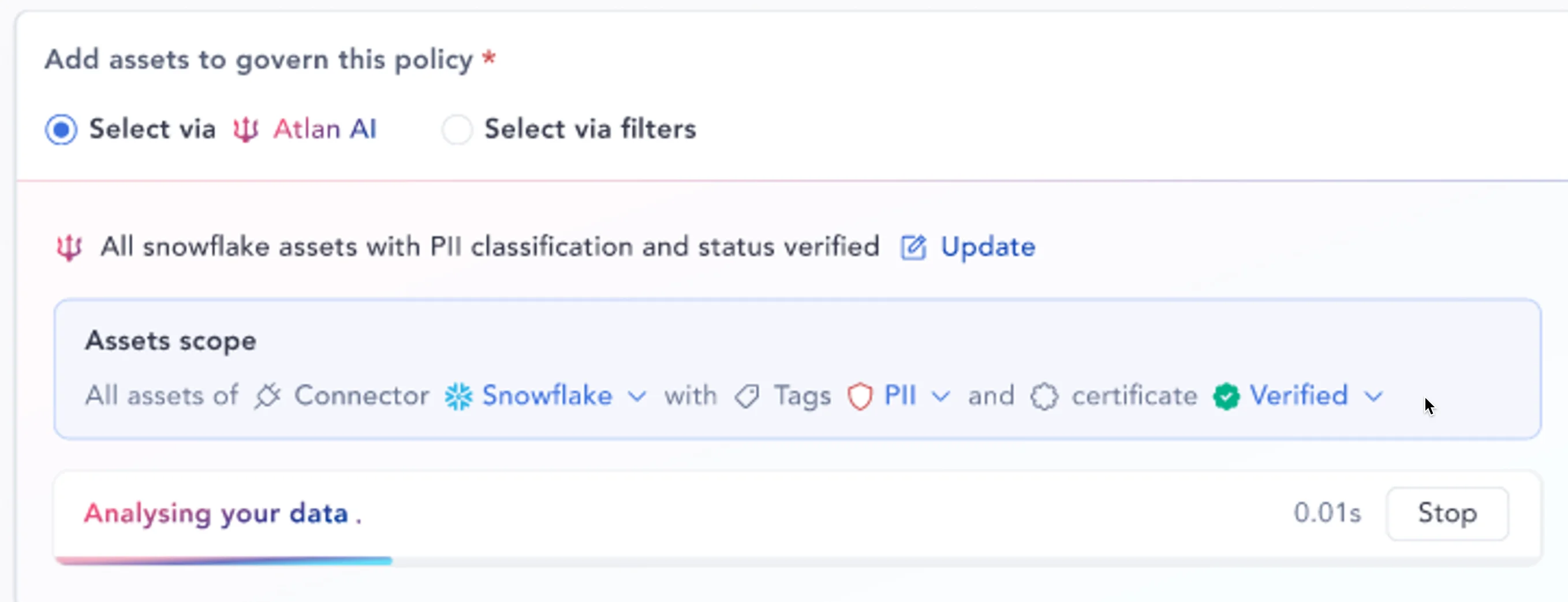
You can draft the policy purpose or scope quickly using Atlan AI — an AI copilot to assist you with documentation, data classification, policy propagation, and more.
After drafting the policy purpose, you can choose the data assets that the policy should govern. Once more, you can use Atlan AI to help speed up this task by auto-suggesting relevant assets.
Atlan also lets you add the technical scope, which goes beyond policy definition and includes details such as the data source, format, tags, and certification status.
This brings policy definition and technical scope under the same umbrella — connecting your data governance policies and establishing a link between the policy’s rules and the specific data sources it governs.

Auto-assigning data assets to relevant data governance policies using Atlan AI - Image by Atlan.
You can attach some business glossary terms to your data governance policy and review them before submitting the policy for approval.
Here’s an example from Atlan: Notice that the policy has a detailed overview, associated business glossary terms, business metrics, etc.
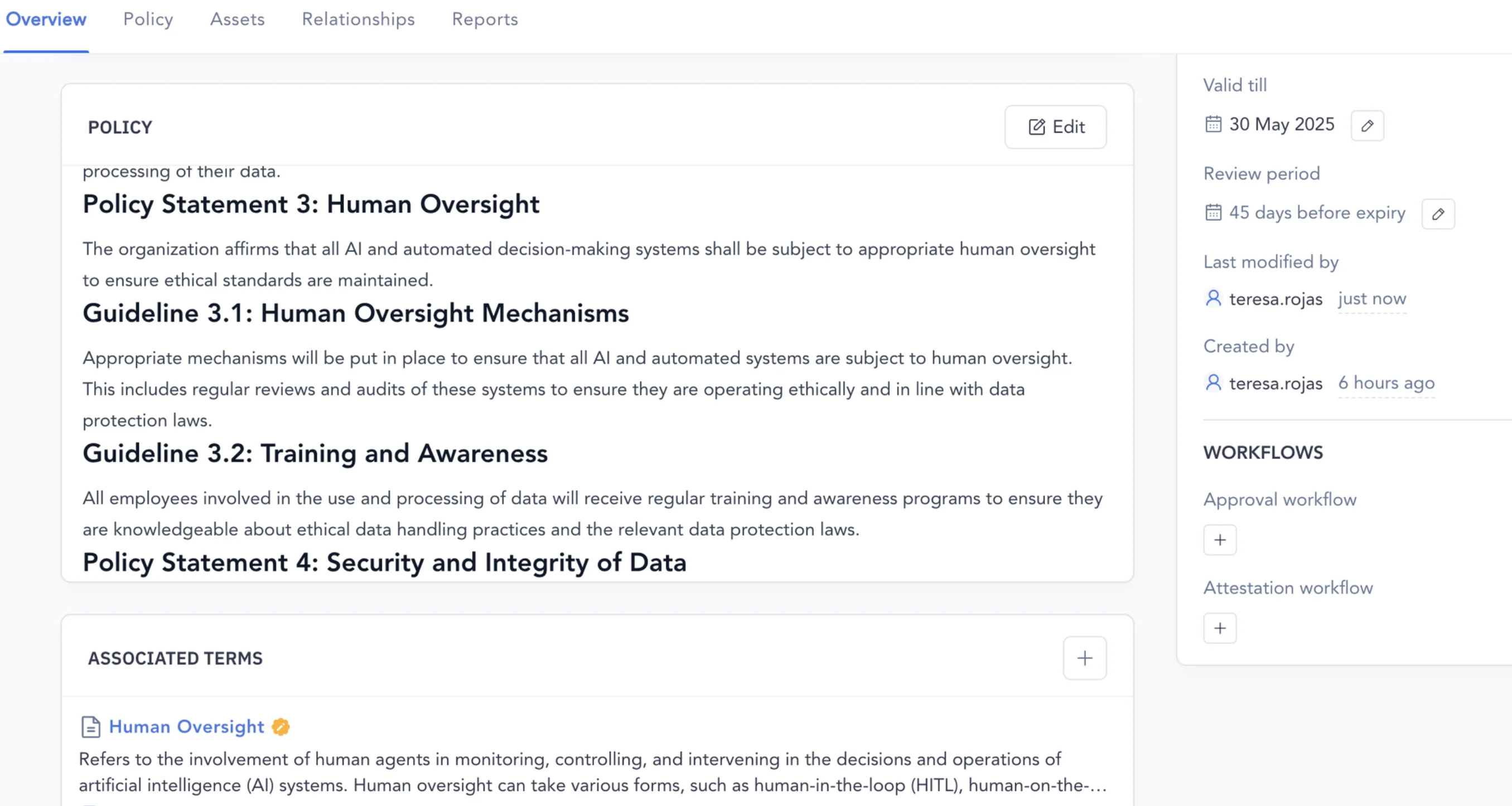
A well-documented data governance policy in Atlan - Image by Atlan.
After submitting your policy, you can track its approval process from the Policy Center homepage.
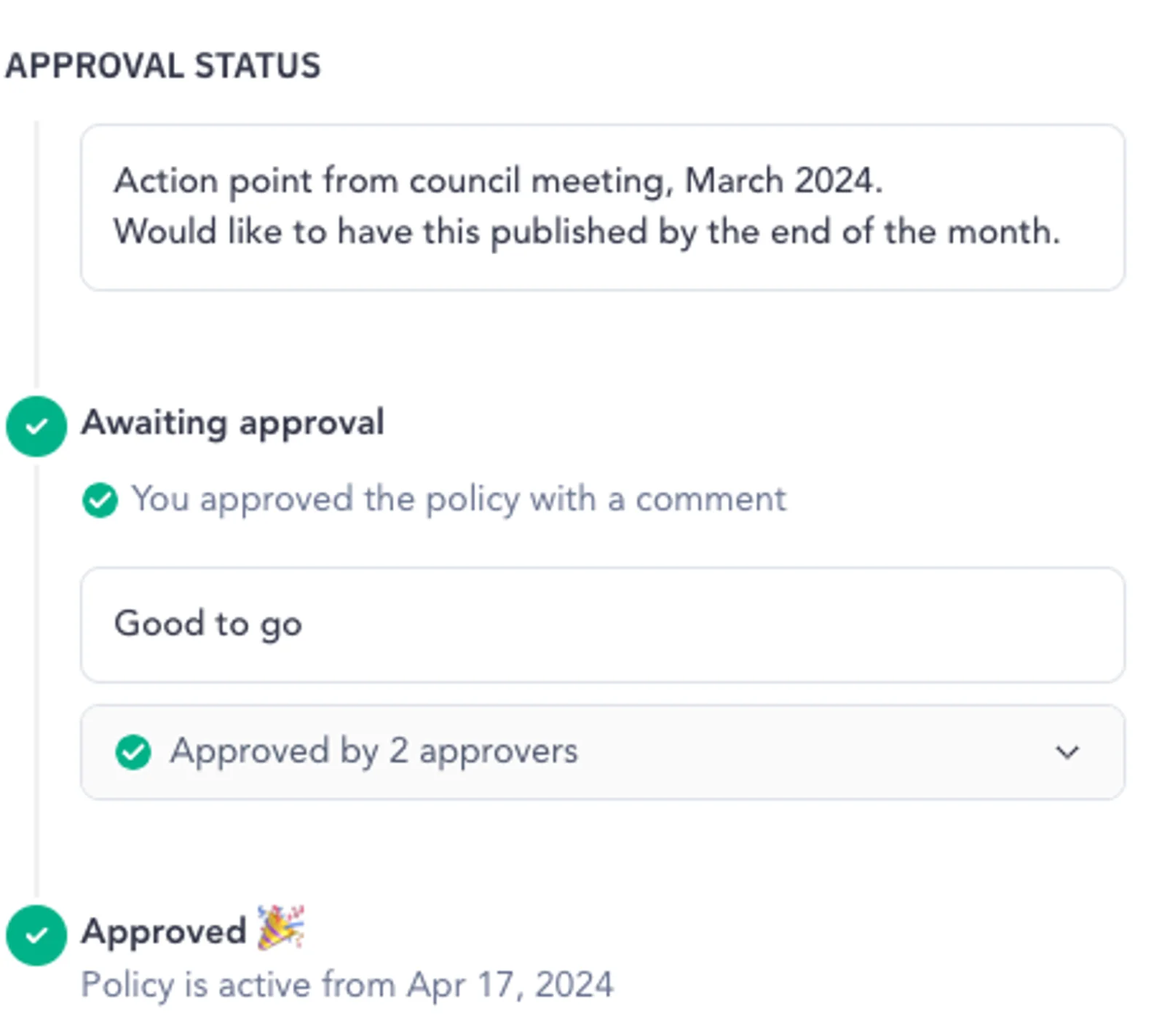
Policy approval status in Atlan - Image by Atlan.
After drafting your policy, you must submit it for approval. This ensures that all the relevant stakeholders have understood, evaluated, and signed off on your data governance policy.
Here’s what a data governance policy approval workflow template looks like in Atlan. The template has automation for policy approval, processes, updates/revisions, and real-time notifications (to be sent to relevant stakeholders).
The templates are predefined and can be configured with drag-and-drop features.
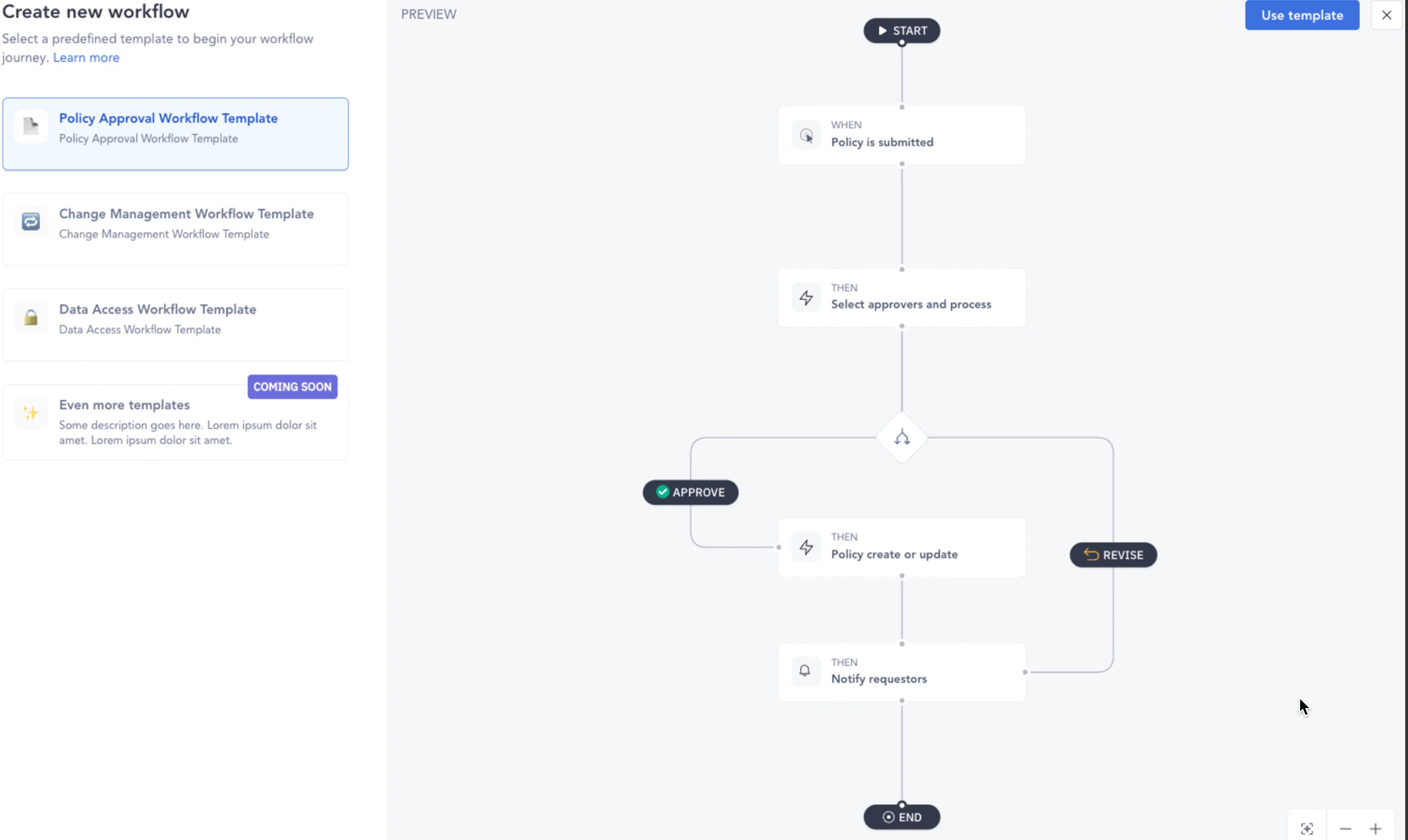
A data governance policy workflow template in Atlan - Image by Atlan.
The approvers, usually business leadership or the data governance committee members, receive all submitted policies in their Atlan Inbox and can review and approve/deny requests from a single location.
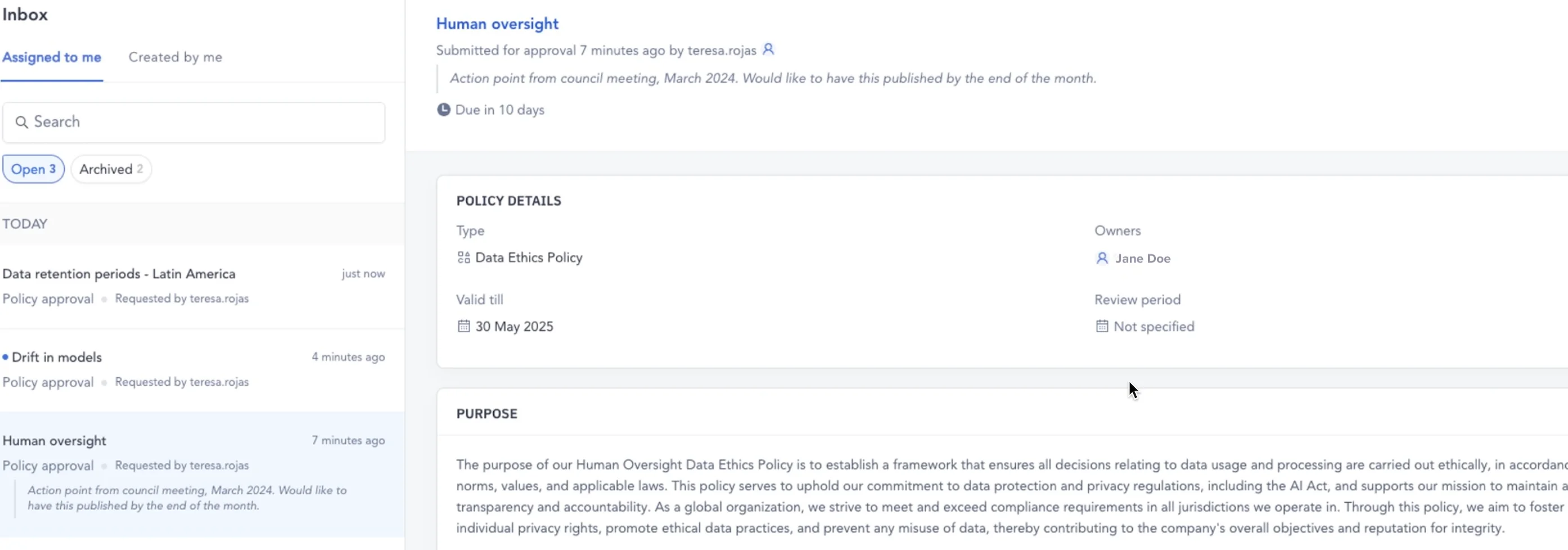
Policy approval messages in Atlan - Image by Atlan.
Once the policy is approved and active, it immediately starts monitoring all the assets it covers. If any assets become non-compliant, an incident will be raised automatically.
So, everything from creating policies to approving and updating them for all data sources can be handled from a single location.
That’s why using an active data governance platform like Atlan is crucial for setting, enforcing, and executing data governance policies at scale, especially for large enterprises with multiple domains and teams spread across regions.
If your organization is in the early stages of establishing best practices and standards around data, knowing where to start with your data governance policy can be challenging. Here are some publicly-available data governance policies you can use as models for your own:
These are just a few examples of what a data governance policy can look like. Pick one that represents your goals and organization communication style most comprehensively, or piece together the strengths of several to serve as your guide to draft your own policy.
You now have a good understanding of a data governance policy, its importance, and the structure and sections it should include. It’s time to start working on your policy.
To help you get started, review this video from the 2022 Data Governance & Information Quality conference for additional insight into the fundamentals of a governance policy.
If you still feel stuck, consider going back to the basics. Check out this overview of data governance and its purpose, benefits, and best practices.