Ways to add, edit, and delete records
There are several ways to update data in an Access database. You add a record to your database when you have a new item to track, such as a new contact to the Contacts table. When you add a new record, Access appends the record to the end of the table. You also change fields to stay up-to-date, such as a new address or last name. To maintain data integrity, the fields in an Access database are set to accept a specific type of data, such as text or numbers. If you don't enter the correct data type, Access displays an error message. Finally, you can delete a record when it is no longer relevant and to save space.
For more information on setting up a database for data entry, see Design considerations for updating data.
In this article
- Updating data by using either a form or datasheet
- Understanding data entry symbols
- Add a record to a table or form
- Find a record
- Delete a record
- Edit data in a text box or field
- Add a date by using the Date Picker
- Apply rich text formatting to data in a Long Text field
- Enter text in a control with input masks
- Enter data by using a list
- Enter zero-length strings
- Undo changes
Updating data by using either a form or datasheet
You use a form to manually update data. Data entry forms can provide an easier, faster, and more accurate way to enter data. Forms can contain any number of controls such as lists, text boxes, and buttons. In turn, each of the controls on the form either reads data from or writes data to an underlying table field.
Datasheets are grids of data that look like Excel worksheets. You can change data by working directly in Datasheet view. If you are familiar with Excel, datasheets should be relatively easy to understand. You can change data in tables, query result sets, and forms that display datasheets. Typically, you use datasheets when you need to see many records at once.
Understanding data entry symbols
The following table shows some of the record selector symbols you might see when updating data and what they mean.
This is the current record; the record has been saved as it appears. The current record is indicated by a change in color in the record selector.
You are editing this record; changes to the record aren't yet saved.
This record is locked by another user; you can't edit it.
This is a new record in which you can enter information.
This is the primary key field and contains a value that uniquely identifies the record.
Add a record to a table or form
- Open the table in Datasheet View or the form in Form View.
- On the Home tab, in the Records group, click New, or click New (blank) record, or press Ctrl+Plus Sign (+).
- Find the record with an asterisk in the record selector, and enter your new information.
- Click or otherwise place the focus on the first field that you want to use, and then enter your data.
- To move to the next field in the same row, press TAB, use the Right or Left arrow keys, or click the cell in the next field. In a table, to move to the next cell in a column, use the Up or Down arrow keys, or click the cell you want.
- When you view another record or close the table or form, Access saves the new record that you added. To explicitly save changes to the current record, press Shift+Enter.
Find a record
You must first find a record before you can edit or delete it. In a form or datasheet that contains only a small number of records, you can use the record navigation buttons to navigate through the records until you find the one you want. When there are many records, you can use the Find and Replace dialog box and filter for the record.
Use the record navigation buttons
You can navigate between records by using the navigation buttons.
Arrow buttons Click to conveniently navigate to the first, previous, next, or last record.
New (blank) record Click to add a record.
Current Record Type a record number and then press ENTER to navigate to that record. The record number is counted sequentially, from the beginning of the form or datasheet — it does not correspond to any field value.
Filter The filter indicator button shows whether a filter has been applied. Click to remove or reapply the filter.
Search Enter text in the Search box. The first matching value is highlighted in real time as you enter each character.
Use the Find and Replace dialog box
The Find and Replace dialog box provides another way to change small amounts of data in less time and with less effort. You can use the Find feature in the Find and Replace dialog box to locate a matching record. When you find a matching record, that record becomes the current record, and you can then edit or delete it.
- Click the field that you want to search.
- On the Home tab, in the Find group, click Find, or press CTRL+F. The Find and Replace dialog box appears.
- Click the Find tab.
- In the Find What box, type the value that you want to match.
- Optionally, use the Look In list to change the field that you want to search, or to search the entire underlying table instead.
- Optionally, in the Match list, select Any Part of Field. Selecting this option provides the broadest possible search.
- In the Search list, select All, and then click Find Next.
Apply a filter
You can apply a filter to limit the records that are displayed to those that match your criteria. Applying a filter makes it easier to find the record that you want to edit or delete.
- Open the table in Datasheet View or form in Form View.
- To ensure that the table or form is not already filtered, on the Home tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Advanced, and then click Clear All Filters, or click Filter in the record navigation bar.
- Navigate to the record that contains the value that you want to use as part of the filter, and then click the field. To filter based on a partial selection, select only the characters that you want.
- On the Home tab, in the Sort & Filter group, click Selection, or right-click the field and apply a filter.
- To filter other fields based on a selection, repeat steps 3 and 4.
Delete a record
The deletion process is fairly simple, except when the record is related to other data and resides on the "one" side of a one-to-many relationship. To maintain data integrity, by default, Access does not let you to delete related data. For more information, see Guide to table relationships.
- Open the table in Datasheet View or form in Form View.
- Select the record or records that you want to delete. To select a record, click the record selector next to the record, if the record selector is available. To extend or reduce the selection, drag the record selector (if it is available), or press SHIFT+DOWN ARROW or SHIFT+UP ARROW.
- Press DELETE, select Home >Records >Delete, or press Ctrl+Minus Sign (-).
Tip If you need to delete only some information but not the entire record, select only the data in each field that you want to delete and then press DELETE.
Edit data in a text box or field
Access provides one text control for use with Short Text and Long Text (also called Memo) fields. Typically, you can tell if the underlying field is short or long text by the size of the control, which usually reflects the size needed for the underlying table field. A Short Text field can store up to 255 characters and a Long Text field can store 64,000 characters.
By design, you cannot edit data from some types of queries. For example, you cannot edit the data returned by a crosstab query, and you cannot edit or remove calculated fields — values that a formula calculates as you use your database, but that do not reside in a table.
- Open the table or query in Datasheet View or form in Form View.
- Click the field or navigate to the field by using the TAB or arrow keys, and then press F2. In Form view, you can click a field's label to select the field. In Datasheet view, you can select a field by clicking near the left border of the field when the mouse pointer becomes a plus (+) sign.
- Place the cursor where you want to enter information.
- Enter or update the text that you want to insert. If you make a typing mistake, press BACKSPACE.
- If a field has an input mask, enter the data according to the format.
- To be more productive, learn the following shortcut keys:
- To insert a new line in a text field, press Ctrl+Enter.
- To insert the default value for a field, press Ctrl+Alt+Spacebar.
- To insert the current date in a field, press CTRL+SEMICOLON.
- To insert the current time, press CTRL+SHIFT+COLON ().
- To check spelling, press F7.
- To reuse similar values of a previous record, move to the corresponding field in the previous record, and then press CTRL+' (apostrophe).
- To explicitly save your changes, press Shift+Enter.
Add a date by using the Date Picker
There are several ways to add a date to your table, and using the Date Picker control is a quick option.
Click the field that you want to add a date to. A calendar icon appears.
- To enter the current date, click Today.
- To select a day in the current month, click the date.
- To select a different month and day, use the forward or back buttons.
Enter text in a control with input masks
A field may have an input mask applied. An input mask is a set of literal and placeholder characters that force you to enter data in a specific format. For more information about input masks, see Control data entry formats with input masks.
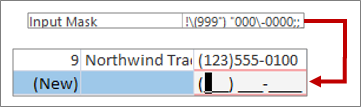
To enter data. follow the input mask:
Apply rich text formatting to data in a Long Text field
If a Long Text field (also called Memo field) supports rich-text formatting, you can apply different fonts, sizes, styles, and colors to your text.
- Open the form in Form View, or the table in Datasheet View.
- Select the Long Text field. Typically, you can look for a field named "Comments," Notes," or "Description."
- On the Home tab, in the Text Formatting group, use the buttons and menus to format the text.
You can apply different fonts and sizes, make text bold or italic, change colors, and so on.
Enter data by using a list
Lists help maintain data integrity and are easy to use. You can use lists in forms, and in tables and queries. Access has three types of lists — value lists, lookup fields and multivalued lists. Value lists display a set of items that you enter manually. Lookup lists use a query to retrieve their data from one or more table result sets open in datasheet view. Multivalued lists solve a common business requirement, a many-to-many relationship. For example, you might to want to track customer support issues and assign multiple people the same issue in one field.
There are three types of list controls:
Multiselect Combo box
Enter an item from a combo box
- Open the form in Form View, or the table or query in Datasheet View.
- Click the down arrow next to the list, and then select the item you want.
- To commit your choice to your database, move the cursor to another field, or press Shift+ Enter.
Enter an item from a list box
- Open the form in Form View.
- Scroll down the list of items in the list box and select the item you want.
- To commit your choice to your database, move the cursor to another field, or press Shift+ Enter.
Enter items from a multivalued list in a Multiselect Combo box
- Open the form in Form View, or the table or query in Datasheet View.
- Click the down arrow next to the list.
- Select up to 100 check boxes, and then click OK.
Edit the items in a list
To edit items in a list, the list must be enabled for editing. For more information, see Design considerations for updating data.
- Open the form, table, or query result set that contains the list.
- Do one of the following:
- Right-click the list that you want to edit, and then click Edit List Items.
- Click the list and then click the button to open the Edit List Items dialog box or form.
- If you are editing a value list or multivalued field, use the Edit List Items dialog box to edit the list data, keeping each item on a separate line, and then click OK after you finish. To select a default value for new records, click the drop-down arrow in the Default Value box, and then click the value you want.
- If you are editing a lookup field, a data entry form appears. Use that form to edit the list data.
Enter zero-length strings
Access allows you to distinguish between two kinds of blank values: Null values and zero-length strings. Null values indicate an unknown value, and zero-length strings indicate fields that contain a space. For example, suppose you have table of customer data, and that table contains a fax number field. You can leave the field blank if you are unsure of a customer's fax number. In that case, leaving the field blank enters a null value, which means you don't know what the value is. If you later determine that the customer doesn't have a fax machine, you can enter a zero-length string in the field to indicate that you know there is no value.
- Open a table or query in Datasheet View or a form in Form View.
- Select the field you want, and then type two double quotation marks with no space between them ("").
- Move the cursor to another record to commit your changes to the database or press Shift+Enter. By default, the quotation marks disappear.
Undo changes
If you type data incorrectly, you can often undo your changes. Do one or more of the following:
- To undo your last changes, select Undo on the Quick Access Toolbar, or press ESC.
- To undo all changes to the record, press ESC again.
- To undo changes after you save changes or move to another record, select Undo on the Quick Access Toolbar. Important As soon as you begin editing another record, apply or remove a filter, or switch to another window or document tab, your changes become permanent.





